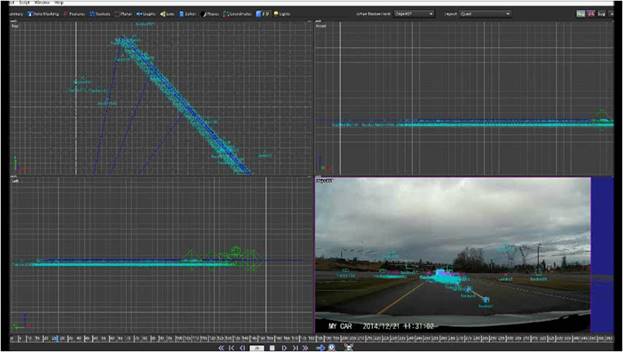
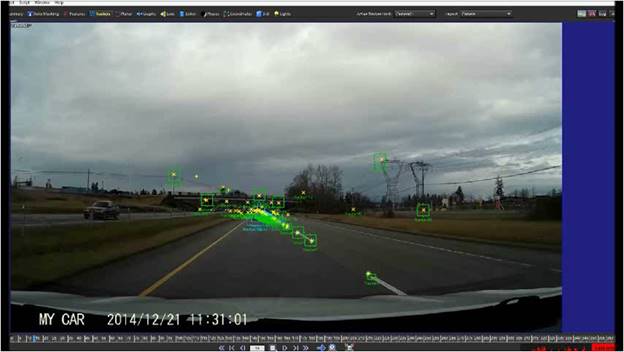
Video Analysis: Accidents can be captured from a wide variety of cameras. Prior to velocity extraction, footage must be converted to an image sequence suitable for further analysis, the precise timing for each frame is then calculated, and the focal length estimated for each image. Video analysis is the first step in investigating captured aircraft, automobile, truck, motorcycle, or bicycle accidents.
Sources: Dash cameras, Red light cameras, Traffic cameras, Security cameras, Web cameras, UAV/aerial footage, Cell phones, Tablets, Photographic cameras, YouTube
Position/Velocity Extraction: Matchmoving techniques are used to determine the exact location and orientation of the camera, whether stationary or moving. Once this is done, additional analysis is conducted to calculate the location of any vehicles visible in the video. Coupled with the temporal analysis, the data reveals motion of the camera and vehicles. Position/velocity extraction provides investigators with critical data evidence to support their investigation.
Data: Instantaneous velocities, Average velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, Lateral Gs, Yaw, Pitch, Angular rotation rate, Skid, Ground track, Airborne flight path, Residual analysis accuracy estimate, Comprehensive video analysis investigation report
Accident Animation: The advantage of video analysis is that it provides its own method of validation. Derived data can be animated in a simulator, then filmed from the calculated camera position. Comparison of this visualization footage against the original video footage intuitively demonstrates how close the solution is to the actual accident parameters, and can be supported by animations from witness perspectives. Animation can also reveal additional aspects of the collision by visualizing the accident from driver or other points of view.
Products: Camera view animation, Top-down / aerial view, Wireframe animation, Fully textured animation, Google Earth animation, Witness point of view animations, Driver point of view animation, Virtual reality animation, Synchronized video and animation, Synchronized video and data display
Accident Site Modelling: Photographs and video of the crash site can be stitched into a 3d point cloud model and used for measurements or additional investigation long after the site has been cleared. The model can also be employed when debriefing the accident investigation or used in animations to tell the complete story of the collision. Accident site modeling provides the opportunity to amalgamate pre-accident motion analysis with post-accident wreckage into an integrated view on the sequence of events.
Products: Collision site point cloud, Textured 3d site model, Google Earth collision site model, Crash site measurements, Crush measurements, Exemplar crush animation
Gyro has developed a large number of special capabilities courtesy of the challenges provided by our clients. These include:
Surveillance camera analysis – Derive the position, movement and speed of a vehicle, pedestrian or other moving object from a stationary surveillance camera.
Velocity of moving camera – Use photogrammetric analysis to determine the position, movement and speed of a camera and the vehicle carrying it.
Velocity of another vehicle – Use photogrammetric analysis to determine the position, movement and speed of another vehicle, pedestrian or other moving object from a stationary or moving camera.
Virtual tire tracks – Use 3D vehicle model to derive the tire path on the road of a vehicle
AI frame rate interpolation – Use artificial intelligence to derive intermediate frames of video in order to transform a low frame-rate video into a natural full frame rate in order to best assess speeds.
AI high definition upscaling – Use artificial intelligence to upscale resolution of video, making it easier to see events in a small portion of the image.
Acceleration/deceleration from video – Derive acceleration and deceleration of vehicles from a video.
Audio spectrum analysis – Conduct audio analysis on a video clip in order to identify warning tones, changes in engine RPM, and extract other audio evidence from a clip.
Video spectrum filtering – Filter video in order to better identify changes in brake lights, signal lights or other visual cues.
Temporal analysis – Identify problems in frame timing synchronize with other videos or events
Stabilization – Stabilize hand-held video or video of another monitor in order to conduct video velocity analysis.
Superimposed data display – Superimpose changing speeds, distances, accelerations or other data onto a video in order to see data in context.
Visualizations – Show correlation between original video and drone/laser scans, surveyed points, or solved vehicle positions and orientation.
Multiple camera solves – Synchronize multiple videos in order to derive vehicle velocity data from multiple sources
Traffic speed analysis – Derive speeds for multiple vehicles in order to determine average traffic speed.
Pedestrian tracking – Match a moving figure to a figure in the video in order to determine pedestrian paths and speeds.
Position extrapolation – Determine position of vehicles and other moving objects if they continued at the same velocity once they left or before they entered the camera view.